lv systolic diameter | Lv end diastolic diameter lv systolic diameter Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium. Check out our louis vuitton luggage cover selection for the very best in unique or custom, handmade pieces from our luggage & travel shops.
0 · normal Lv end systolic dimension
1 · normal Lv end diastolic diameter
2 · left ventricular internal dimension diastole
3 · left ventricular diameter chart
4 · left ventricle size chart
5 · left internal dimension in systole
6 · Lv systolic diameter mm
7 · Lv end diastolic diameter
The Best CPUs for Gaming in 2024. Buying the right processor for PC gaming might seem complicated—especially with AMD's multiple Ryzen families and Intel's many Cores and "Lakes." Here's.
normal Lv end systolic dimension
The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the .
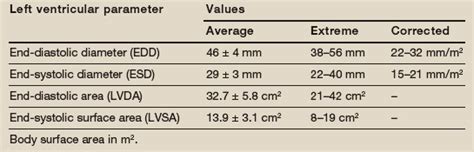
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.Ejection Fraction (EF) (see below) is the predominant method for assessing global systolic function (see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end . The LV diameter is a measure that can be easily obtained during echocardiography at the time of LVEF measurement. Previous studies have established the importance of LV size with regard to cardiac mortality.
chanel two toned heels
normal Lv end diastolic diameter
Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium.
Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no . Learn how to assess LV systolic function using echocardiography, including linear, area, and volume measurements. LV end systolic diameter (LVESD) is one of the parameters used to calculate ejection fraction and . LV global systolic function is generally assessed by measuring the difference between the end-diastolic and end-systolic value divided by the end-diastolic value. This can be applied for either a one-dimensional 2D image or .Measurements of the left ventricle can be obtained by the MMode or by 2D methods. 3.2.2.1.1 MMode measurements / Diameter. MMode still is the most widely used the technique. The reasons are historical. MMode was the first .
The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the chordae.
Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.Ejection Fraction (EF) (see below) is the predominant method for assessing global systolic function (see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). Global Longitudinal Strain is a new parameter to assess LV systolic function. LV Volumes used to calculate EF The LV diameter is a measure that can be easily obtained during echocardiography at the time of LVEF measurement. Previous studies have established the importance of LV size with regard to cardiac mortality.
Measures of left ventricular (LV) size obtained in a 36-year-old man, body surface area 2 m 2. LV internal diameter in diastole measured in the normal range (5.6 cm); indexed volume was severely dilated (LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) 200 .Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium.Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no significant wall motion abnormalities.
chanel tv documentary
The measurements required for this quantitative estimate of systolic function are LV internal diameter at end diastole (LVIDd, also called end diastolic diameter LVEDD) and LV internal diameter at end systole (LVIDs, also called end systolic diameter LVESD).
LV global systolic function is generally assessed by measuring the difference between the end-diastolic and end-systolic value divided by the end-diastolic value. This can be applied for either a one-dimensional 2D image or in 3D.
Measurements of the left ventricle can be obtained by the MMode or by 2D methods. 3.2.2.1.1 MMode measurements / Diameter. MMode still is the most widely used the technique. The reasons are historical. MMode was the first technique of echocardiography.
The LV dimensions must be measured when the end-diastolic and end-systolic valves (MV and AoV) are closed in the parasternal long axis (PLAX) view. The measurement is performed in the basal portion of the LV by the chordae.Normal (reference) values for echocardiography, for all measurements, according to AHA, ACC and ESC, with calculators, reviews and e-book.Ejection Fraction (EF) (see below) is the predominant method for assessing global systolic function (see below) and is derived from the LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) and LV end-systolic volume (LVESV). Global Longitudinal Strain is a new parameter to assess LV systolic function. LV Volumes used to calculate EF The LV diameter is a measure that can be easily obtained during echocardiography at the time of LVEF measurement. Previous studies have established the importance of LV size with regard to cardiac mortality.
Measures of left ventricular (LV) size obtained in a 36-year-old man, body surface area 2 m 2. LV internal diameter in diastole measured in the normal range (5.6 cm); indexed volume was severely dilated (LV end-diastolic volume (LVEDV) 200 .Left ventricular systolic function can be assessed by quantifying the rate of change of the mitral regurgitant jet, with normal function showing a rapid increase in LV pressure into the low-pressure left atrium.
Fractional shortening (FS) is calculated by measuring the change (% reduction) in left ventricular diameter during systole. It is considered a poor measure of systolic function; it is only reliable if the left ventricle has normal geometry and no significant wall motion abnormalities. The measurements required for this quantitative estimate of systolic function are LV internal diameter at end diastole (LVIDd, also called end diastolic diameter LVEDD) and LV internal diameter at end systole (LVIDs, also called end systolic diameter LVESD). LV global systolic function is generally assessed by measuring the difference between the end-diastolic and end-systolic value divided by the end-diastolic value. This can be applied for either a one-dimensional 2D image or in 3D.

left ventricular internal dimension diastole
LOUIS VUITTON Official site - Discover our latest Bags's Coussin in For Women LV Icons collections, exclusively on louisvuitton.com and in Louis Vuitton Stores.
lv systolic diameter|Lv end diastolic diameter