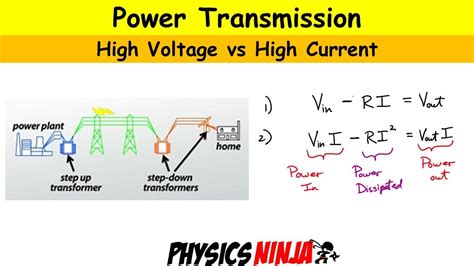
lv vs hv | hv vs Lv distribution lv vs hv High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a . The historical period of ancient Greece is unique in world history as the first period attested directly in comprehensive, narrative historiography, while earlier ancient history or protohistory is known from much more fragmentary documents such as annals, king lists, and pragmatic epigraphy.
0 · voltage rating chart
1 · hv vs Lv distribution
2 · difference between hv and Lv cable
3 · Lv vs hv electrical
4 · Lv vs hv cable
5 · Lv mv hv voltage ranges
6 · Lv and mv switchgear
7 · Lv and hv in transformer
Keep in mind that it's saying 2% of your DNA is similar to the DNA found in the Malta reference panel, not that you have ancestors from there or whatnot. This is very normal .

The HV/LV Safe Working Practice Guidance course at EPIT is ideal for those seeking to deepen their understanding of safe working practices in both high and low voltage environments. This course provides updated guidance on safety protocols, isolation procedures, and HV/LV .High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a .In this post, we will see some basic differences between two widely used cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage). Both these cables use copper and aluminium as conductor .In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?
Low and high voltage refers to the intensity at which electricity is sent through wires. Low voltage is less likely to cause damage or injury, while high voltage is more dangerous. While low voltage is generally safe, some . Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article .High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables . The primary distinction between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables lies in their construction and insulation properties. High-voltage cables are designed with multiple .
In this post, we will see some basic differences between two widely used cables - HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage). Both these cables use copper and aluminium as .The HV/LV Safe Working Practice Guidance course at EPIT is ideal for those seeking to deepen their understanding of safe working practices in both high and low voltage environments. This course provides updated guidance on safety protocols, isolation procedures, and HV/LV switching. Participants gain insights into the latest industry standards .
voltage rating chart
High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.In this post, we will see some basic differences between two widely used cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage). Both these cables use copper and aluminium as conductor alloys. Table of Contents. HV Cables. HV cables are used for a very high voltage transmission; typically used in power plants and transformers.In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?PVC, XLPE, rubber, and control cables are commonly used for LV applications, while XLPE, oil-filled, and gas-insulated cables are used for HV applications. Understanding the different types of LV and HV cables is critical in selecting the right cable for a specific application.
Low and high voltage refers to the intensity at which electricity is sent through wires. Low voltage is less likely to cause damage or injury, while high voltage is more dangerous. While low voltage is generally safe, some safety measures should still be taken. Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article explores these classifications and their applications, highlighting their differences and relevant products from Blue Jay.
High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power . The primary distinction between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables lies in their construction and insulation properties. High-voltage cables are designed with multiple semiconductor and shielding layers, which significantly exceed the . In this post, we will see some basic differences between two widely used cables - HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage). Both these cables use copper and aluminium as conductor alloys. HV Cables . HV cables are used for a very high voltage transmission; typically used in power plants and transformers. It will vary between 33kV to 220kV.
The HV/LV Safe Working Practice Guidance course at EPIT is ideal for those seeking to deepen their understanding of safe working practices in both high and low voltage environments. This course provides updated guidance on safety protocols, isolation procedures, and HV/LV switching. Participants gain insights into the latest industry standards .High (HV), Extra- High (EHV) & Ultra-High Voltages (UHV) - 115,000 to 1,100,000 VAC. Medium Voltage (MV) - 2,400 to 69,000 VAC. Low Voltage (LV) - 240 to 600 VAC. Generac issued a white paper titled Medium Voltage On-Site Generation Overview. The white paper compares NEC to ANSI Standards.In this post, we will see some basic differences between two widely used cables – HV (High Voltage) and LV (Low Voltage). Both these cables use copper and aluminium as conductor alloys. Table of Contents. HV Cables. HV cables are used for a very high voltage transmission; typically used in power plants and transformers.
In this blog, we present the definition of LV, MV and HV, the differences between voltages and their usage areas and more for you. What is the definition of Low Voltage, Medium Voltage and High Voltage?PVC, XLPE, rubber, and control cables are commonly used for LV applications, while XLPE, oil-filled, and gas-insulated cables are used for HV applications. Understanding the different types of LV and HV cables is critical in selecting the right cable for a specific application.
hv vs Lv distribution
Low and high voltage refers to the intensity at which electricity is sent through wires. Low voltage is less likely to cause damage or injury, while high voltage is more dangerous. While low voltage is generally safe, some safety measures should still be taken.
Voltage classifications typically include Low Voltage (LV), Medium Voltage (MV), and High Voltage (HV), each serving distinct purposes in power distribution and usage. This article explores these classifications and their applications, highlighting their differences and relevant products from Blue Jay.
High Voltage (HV): between 45 kV and 230 kV. Extra High Voltage (EHV): from 230 kV and above. As a general rule, LV cables might be used in applications like fixed wiring; MV cables are critical power distribution (both for local grid power and for heavy-duty equipment); HV cables are aerial cables - overhead line for widescale power . The primary distinction between high-voltage (HV) and low-voltage (LV) cables lies in their construction and insulation properties. High-voltage cables are designed with multiple semiconductor and shielding layers, which significantly exceed the .
difference between hv and Lv cable
Lv vs hv electrical
Chetro Ketl is an archaeological site, and the ancient ruins of an Ancestral Puebloan settlement, located in the Chaco Culture National Historical Park, New Mexico, United States of America. Chetro Ketl .
lv vs hv|hv vs Lv distribution