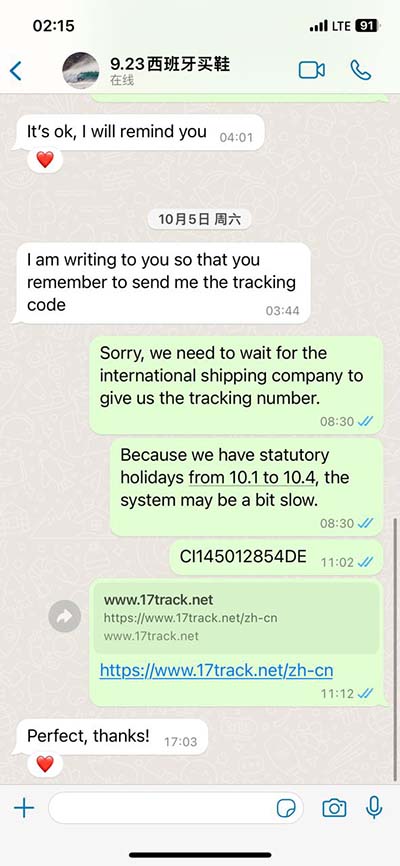
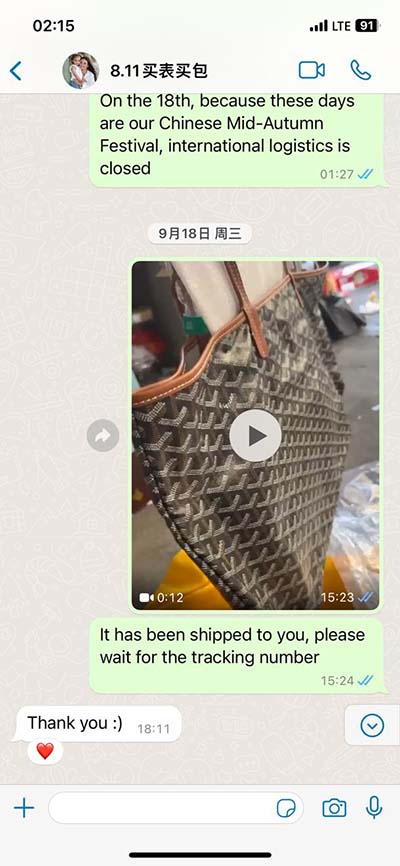
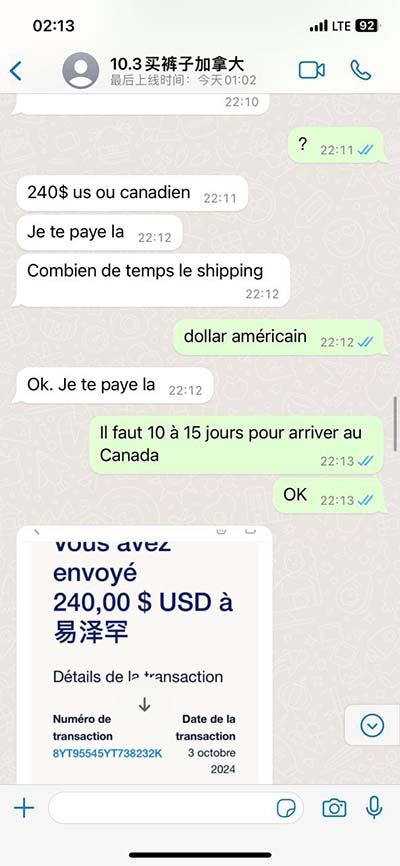
lv segment echo | 17 wall segments echo lv segment echo Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to calculate the LV wall motion score index (sum score of all segments assessed / # segments assessed). . LV. Mani pasūtījumi. +371 67 202 000. 24/7 atbalsta dienests. Mūsu atbalsta dienests palīdzēs jums rezervēt ceļojumu tiešsaistē (online). Ja jums rodas kāds jautājums ceļojuma laikā, tad ziniet – mēs esam pieejami saziņai visu diennakti un radīsim risinājumu vai atbildi visīsākajā laikā. Minimālais avansa maksājums.
0 · what is fractional shortening echo
1 · normal Lv size and function
2 · left ventricular segmentation diagram
3 · how to assess Lv function
4 · Lv wall thickness echo
5 · Lv wall segments echo
6 · 17 wall segments echo
7 · 17 segments of the heart
Ejection fraction typically refers to the left side of the heart. It shows how much oxygen-rich blood is pumped out of the left ventricle to most of the body’s organs with each contraction. LVEF helps determine the severity of dysfunction on the left side of the heart.
Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six .Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to calculate the LV wall motion score index (sum score of all segments assessed / # segments assessed). .The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as .Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the .
Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these .echocardiographic techniques used in the evaluation of left ventricular systolic function. In particular, we focus on the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography, including its utility in the .
LV Function and Haemodynamic Assessment Echocardiography. SYSTOLIC FUNCTION. Global Function. stroke volume: end-diastolic volume – end-systolic volume. .Several echocardiographic measurements are available to assess left ventricular systolic function. These methods elucidate slightly different aspects of systolic function and their combined use .Echocardiography is the principal modality for investigating left ventricular systolic function and diastolic function. M-mode, 2D echocardiography and Doppler are all used to examine various .
The 17 segment model adds an apical segment to the left ventricle. In absence of a 17th segment, ischemia of the apical portion of the left ventricle was disproportionately represented in the wall .Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each.
Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to calculate the LV wall motion score index (sum score of all segments assessed / # segments assessed). Regional Wall Motion during Infarction and IschemiaThe LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as segment 17. The 17 segments correspond to specific coronary artery territories (1).Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .
Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each.echocardiographic techniques used in the evaluation of left ventricular systolic function. In particular, we focus on the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography, including its utility in the detection of subclinical left ventricular dysfunction and the associated prognostic implications. LV Function and Haemodynamic Assessment Echocardiography. SYSTOLIC FUNCTION. Global Function. stroke volume: end-diastolic volume – end-systolic volume. cardiac output: Q = SV X HR. = (Aortic Area x V x Tej) x HR. Q .
Several echocardiographic measurements are available to assess left ventricular systolic function. These methods elucidate slightly different aspects of systolic function and their combined use allows for careful mapping of systolic function.Echocardiography is the principal modality for investigating left ventricular systolic function and diastolic function. M-mode, 2D echocardiography and Doppler are all used to examine various parameters. The aim of this Review is to outline the broad principles of transthoracic echocardiography, including the traditional techniques of two-dimensional, colour, and spectral Doppler.Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each.
Semi quantitative wall motion score (1-4) can be assigned to each segment to calculate the LV wall motion score index (sum score of all segments assessed / # segments assessed). Regional Wall Motion during Infarction and Ischemia
The LV is divided into 3 sections: base, mid-cavity, and apex; and further subdivided into 17-segments: 6 basal segments, 6 mid-cavity segments, 4 apical segments, and the true apex as segment 17. The 17 segments correspond to specific coronary artery territories (1).Assessment of left ventricular systolic function has a central role in the evaluation of cardiac disease. Accurate assessment is essential to guide management and prognosis. Numerous echocardiographic techniques are used in the assessment, each .
Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for echocardiography. The left ventricle is divided into 17 segments for 2D echocardiography. One can identify these segments in multiple views. The basal part is divided into six segments of 60° each.echocardiographic techniques used in the evaluation of left ventricular systolic function. In particular, we focus on the role of speckle-tracking echocardiography, including its utility in the detection of subclinical left ventricular dysfunction and the associated prognostic implications. LV Function and Haemodynamic Assessment Echocardiography. SYSTOLIC FUNCTION. Global Function. stroke volume: end-diastolic volume – end-systolic volume. cardiac output: Q = SV X HR. = (Aortic Area x V x Tej) x HR. Q .
what is fractional shortening echo
Several echocardiographic measurements are available to assess left ventricular systolic function. These methods elucidate slightly different aspects of systolic function and their combined use allows for careful mapping of systolic function.Echocardiography is the principal modality for investigating left ventricular systolic function and diastolic function. M-mode, 2D echocardiography and Doppler are all used to examine various parameters.

burberry glasses frame broken
burberry glasses be1006 height
In this article, we consider large LV models with random parameters. Lever-aging on the asymptotic understanding of large random matrices which naturally appear enables us to provide insights on equilibria and species coexistence for such models. Model and assumptions. Large Lotka-Volterra systems of di erential equations arise in various scienti c
lv segment echo|17 wall segments echo